sUAS Operation Limitations
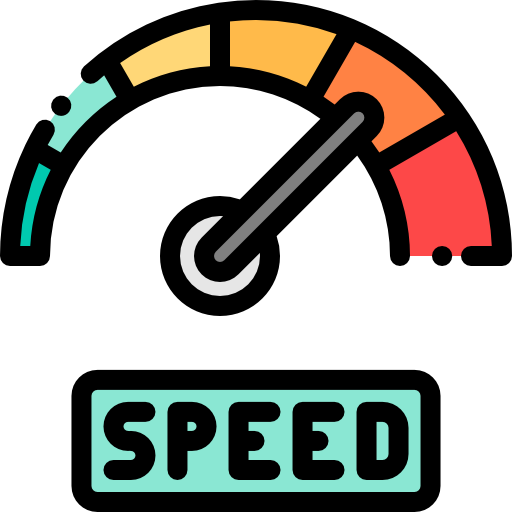

Maximum Speed: 87 knots (100mph)
The sUAS is not allowed to fly faster than 87 knots (100 mph).
Minimum Visibility: At least 3 statute miles.
Visibility refers to the distance a pilot can see and identify objects on the ground and in the airspace.
This means that the remote pilot must be able to see the drone and any other aircraft in the vicinity clearly.
By the way, “statute miles” means regular land miles — the ones we use on roads and maps in the U.S.
- 1 statute mile = 5,280 feet
- It’s called “statute” to distinguish it from nautical miles, which are used in other specific aviation and maritime navigation purposes.
Field Example: Ocean Ecology Mission
You’re out on the coast to document dune restoration and seabird activity with your drone. Before launching, you check the weather and see visibility is reported at 2 statute miles. Even though the fog looks light, you know FAA regulation rules require at least 3 statute miles of visibility, so you hold off on flying until conditions improve.
Later that morning, visibility increases to 6 statute miles. You run a quick preflight check, confirm you’re good to go, and begin safely capturing your coastal footage within legal limits.

Cloud Clearance: 500 feet below, 2,000 feet horizontally
The sUAS must stay at least 500 feet below a cloud and 2,000 feet horizontally away from a cloud. This reduces the chance of flying into clouds that could block their view.
Field Example: Coastal Wetland Survey
You’re flying your drone along a marshy coastline to document plant health and water levels. As you prep for launch, you notice a low cloud layer hovering above. You check your weather report and estimate the cloud base is around 800 feet AGL—since you’re only flying up to 300 feet, you’re well within the rule to stay at least 500 feet below the clouds.
You also confirm that no clouds are drifting close horizontally—keeping at least 2,000 feet of space to ensure clear visibility and safe flying conditions.

Altitude Restriction: Max Height of 400 ft AGL
The sUAS cannot fly higher than 400 feet above ground level (AGL).
That said, inspecting a structure such as a tower, you’re allowed to fly within a 400 foot radius of the structure, including the structure’s topmost point.
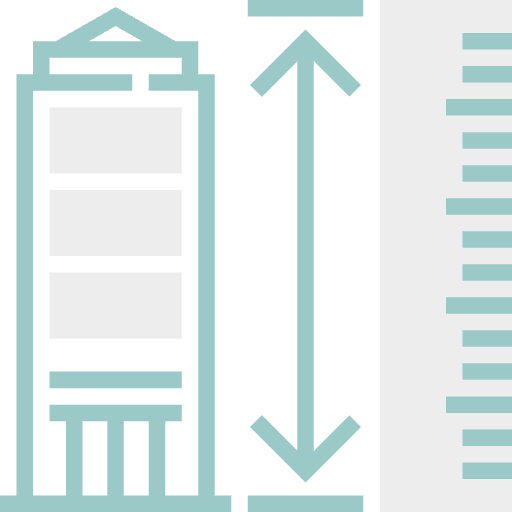
Tower Inspection Altitude Restrictions: Within 400 ft radius of structure’s topmost point
The sUAS can fly within a 400 foot radius (vertically and horizontally) of a structure’s topmost point.
Field Example: Cell Tower Inspection
You’re on-site to inspect a 200-foot tall cell tower in a rural area. Under Part 107 rules, you’re allowed to fly your drone up to 400 feet above the top of the structure, meaning your max flight altitude here is 600 feet AGL. You also stay within 400 feet horizontally of the tower to remain compliant while capturing close-up visuals of the tower.





